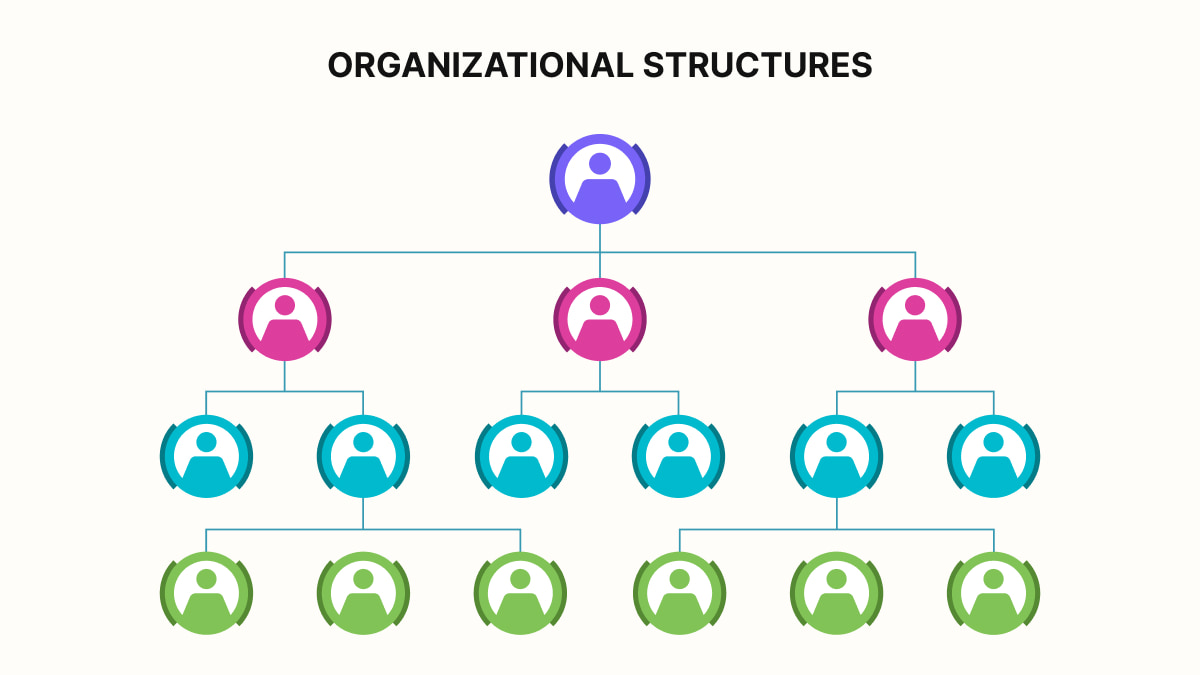
An organizational framework is a system that defines how a company structures its various components. This includes employees, assignments and a uthority.
This system effectively aids in reaching the objectives. It's similar to a framework of a business, it offers the system that underpins its activities. An effectively created one is essential for productivity:
- Interaction
- Decision-making
- Overall tasks within the company
There are several types of organizational structures. They have pros and cons, so the best choice for each company relies on important factors. They encompass the size, sector, culture, and objectives of an organization. Understanding these various kinds is crucial for leaders to make right decisions and establish their structural design.
Understanding the Concept of Organizational Structures
As mentioned earlier, organizational structures are systems. It defines how a company organizes its people, tasks, and authority. Essentially, it defines how roles, responsibilities, and power are usually distributed within the company.
A good system offers many pros for a company. What are they? Here they are:
- Efficient Decision-Making
- Better Communication
- Improved Coordination
- Increased Accountability
- Better Resource Allocation
- Enhanced Adaptability
In essence, the organizational system is the backbone of any successful company. It provides a clear framework for operations and ensures smooth workflow, effective decision-making, and efficient resource allocation.
Key Features of Organizational Structures
What are the key features of organizational structure ? A typical one is usually characterized by the following features:
- Hierarchy. This refers to the levels of authority and accountability within an organization. It outlines who reports to whom and who can make choices.
- Departmentalization. It involves grouping similar tasks or functions into specific departments, for example, marketing, finance, and operations.
- Span of Management. This refers to the number of people a manager can effectively supervise.
- Centralization and Decentralization. Centralization concentrates decision-making authority at the top, while decentralization distributes it throughout lower levels.
- Formalization. This refers to the degree to which rules, procedures, and policies are documented and enforced.
As a result, a business’s system is a critical component. You must carefully consider:
- Hierarchy
- Departmentalization
- Span of management
- Centralization/decentralization
- Formalization
Benefits of Having an Organizational Structure
An organizational structure serves as the backbone of any firm, it, for example, provides a framework that defines roles, responsibilities, and reporting relationships. This system is essential. It’s for efficient work, clear communication, and effective choices. So, let’s take a closer look at the benefits:
- Improved Communication. Clear lines of authority and communication channels facilitate efficient information flow.
- Enhanced Coordination. A structured approach ensures that different teams and departments work together seamlessly.
- Increased Efficiency. By streamlining processes and cutting redundancies, organizations can boost productivity.
- Better Decision-Making. A clear hierarchy and defined roles enable faster and more informed decision-making.
- Enhanced Accountability. With clear responsibilities assigned to individuals, accountability is improved.
- Improved Morale. A business can boost employee morale by providing clarity, fairness, and opportunities for growth.
- Greater Adaptability. A flexible system can adapt to changing market conditions and industry trends.
- Stronger Brand Identity. A well-defined system can help maintain a consistent brand image and messaging.
Understand the fundamental features and pros of these systems. Then, your company can construct robust frameworks that propel growth, innovation, and success. These frameworks serve as the backbone of efficient operations. It enables businesses to streamline processes, set resource allocation, and make data-driven choices.
Ultimately, a well-designed system fosters a culture of continuous improvement. It empowers companies to adapt to changing business environment dynamics and keep a competitive edge.
The 4 Most Common Types of Organizational Structures
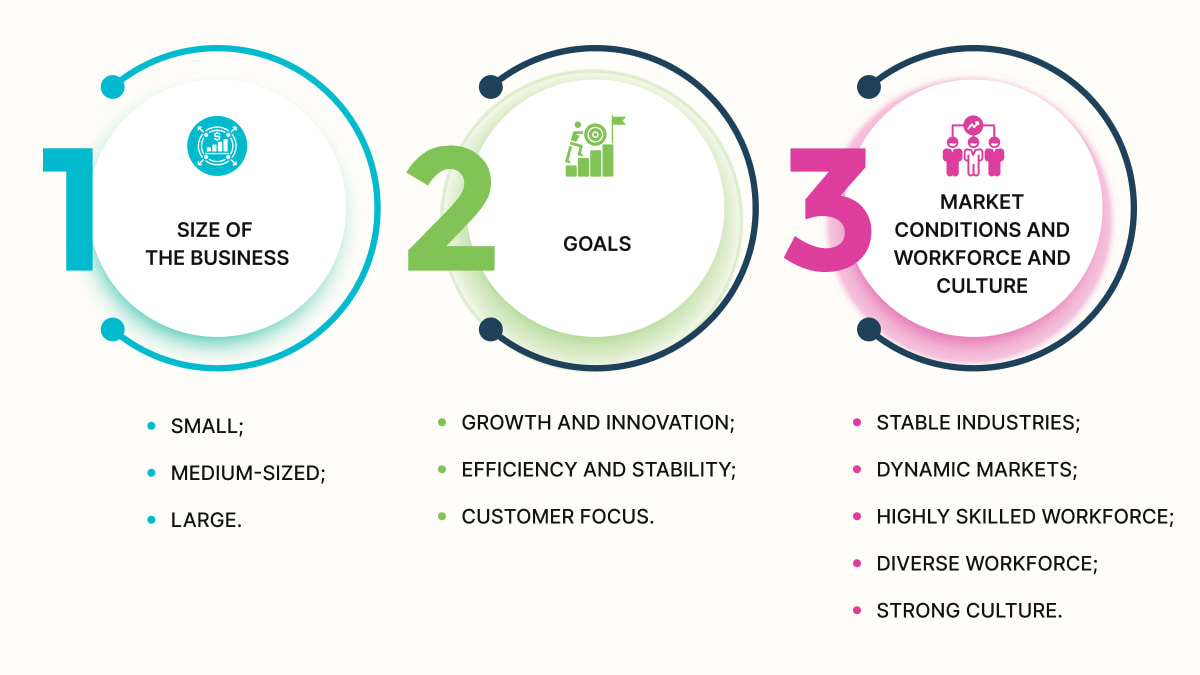
These hierarchy systems are the backbone of any organization. They define how roles, responsibilities, and power are usually distributed within a company. Here are four of the most common types.
Functional. This one groups employees based on their specific functions or roles. They are marketing, finance, operations, and human resources. Each department operates independently. There is a clear chain of command.
- Example. A small tech startup may have a functional system with departments for engineering, product management, and sales.
Divisional. Among different organizational structures, in this one, the company is usually divided into self-contained divisions. It's often based on product lines, geographic regions, or client segments. Each operates as a separate unit with its own functions.
- Example. A multinational corporation might have divisions for North America, Europe, and Asia. Each has its own marketing, sales, and operations teams.
Matrix. This type mixes elements of functional and divisional systems. Employees report to two managers: a functional and a project manager. This system is often used in project-based companies or when cross-functional collaboration is crucial.
- Example. A consulting business might use a matrix system to assign consultants to many projects. Meanwhile, it still maintains functional expertise in industries like strategy, finance, and tech.
Flat. Among different types of organizational structures, this one has few or no levels of middle management. This decentralized approach empowers employees to make choices and solve problems quickly. It's often used in smaller companies or those that focus on innovation and agility.
- Example. A tech startup may have a flat system. There are teams organized around specific products or projects. Employees have direct access to the CEO and other senior leaders.
However, the choice of system depends on many factors. It includes the company’s size, industry, culture, and goals. A well-designed system can significantly impact an organization's efficiency, productivity, and overall success.
Emerging and Hybrid Organizational Structures
The business landscape continues to evolve. So, traditional systems are giving way to more flexible and adaptive ones. These examples of organizational structures include emerging and hybrid systems. They’re to respond to the demands of the digital age. It's characterized by rapid change, innovation, and globalization.
Agile companies are characterized by their ability to respond quickly to change. They emphasize iterative development, collaboration, and continuous improvement. Key features of agile business include:
- Self-Organizing Teams. They can make choices and solve problems independently.
- Iterative Development. Projects are small, manageable iterations. It allows for flexibility and adaptability.
- Continuous Delivery. Organizations focus on delivering value to clients frequently.
Now, let’s take a closer look at team- and project-based systems:
| Team-Based | Project-Based |
|---|---|
| Those systems prioritize teams as the primary unit of work. They’re cross-functional, bringing together individuals with diverse skills and expertise. This approach fosters collaboration, innovation, and employee engagement.
What are key features of this organizational structure? They are: |
These systems are designed to manage specific projects or initiatives. Teams are usually formed to work on these projects. And they’re dissolved once the project is complete. This system is particularly well-suited for companies that operate in project-based industries. For example, consulting, engineering, and construction.
Key Features: |
| Empowered Teams. Teams have the autonomy to make choices and solve problems. | Temporary Teams. Teams are usually formed for specific projects. |
| Shared Leadership. Leadership is distributed among team members. | Matrix Management. Employees may report to both functional and project managers. |
| Cross-Functional Collaboration. Teams are composed of individuals from different departments. | Focus on Project Delivery. The primary goal is to deliver successful projects. |
Among the different types of organizational structures, these ones are what offer several pros. It includes increased agility, improved employee engagement, and enhanced innovation. By embracing these new models, organizations can better adapt to the challenges and opportunities of the modern world.
How to Choose the Right Structure for Your Organization
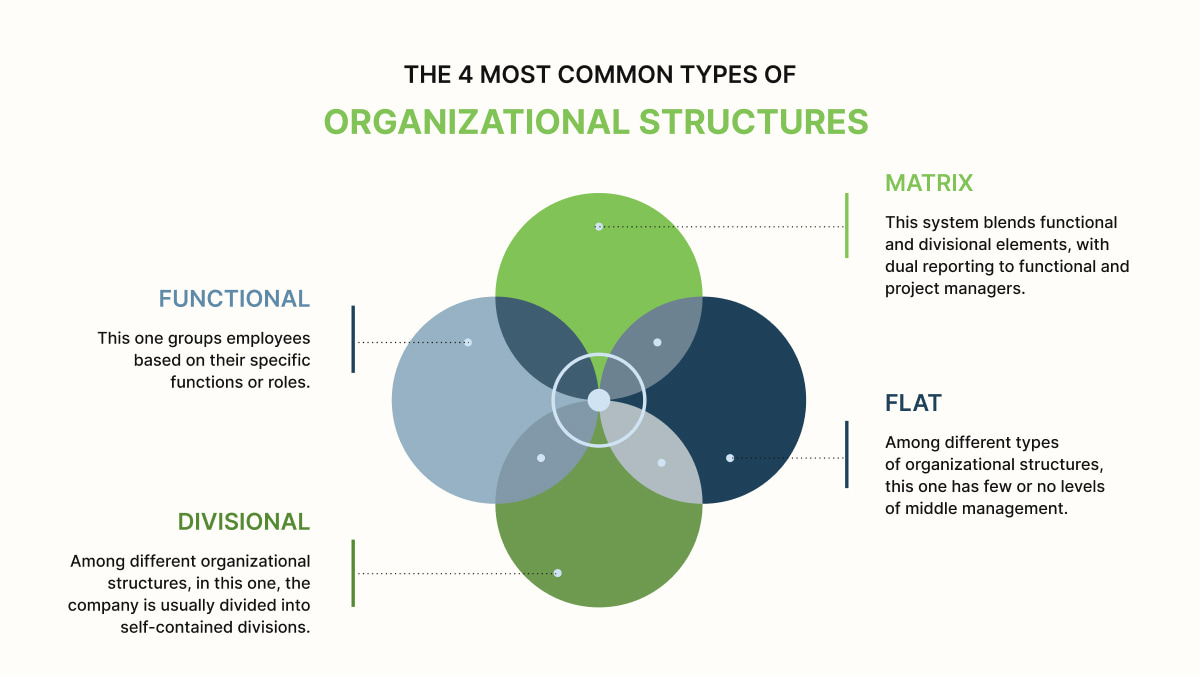
Selecting the appropriate system is a critical choice. It can significantly impact a company's work. To make an informed choice, consider 3 factors when choosing the type of organizational structure.
1. Size of the Business:
- Small. Smaller companies often benefit from simpler, flat systems. These promote flexibility and rapid decision-making. A functional or divisional one may be sufficient for management operations.
- Medium-Sized. As organizations grow, more complex systems may be necessary to manage increased complexity. A matrix system, for example, can balance functional expertise with project-based teams.
- Large. Large businesses typically adopt hierarchical systems with multiple layers of management. It’s to coordinate diverse operations. Divisional systems can be effective for controlling geographically dispersed or product-based companies.
2. Goals:
- Growth and Innovation. Among different types of organizational structures, flat or team-based systems can foster creativity and rapid decision-making. Companies focused on growth and innovation may benefit from a more decentralized system. It empowers employees to take risks and experiment.
- Efficiency and Stability. Organizations prioritizing efficiency and stability may prefer a more centralized, bureaucratic system. It emphasizes standardization and management.
- Customer Focus. Customer-centric businesses may adopt a divisional system organized around customer segments or geographic regions. It’s to improve responsiveness and satisfaction.
3. Market conditions and Workforce and Culture:
- Stable Industries. More traditional, hierarchical systems may be suitable.
- Dynamic Markets. Agile, team-based, or matrix systems can help companies adapt to rapid change.
- Highly Skilled Workforce. Flat or team-based systems can empower employees and leverage their expertise.
- Diverse Workforce. Matrix systems can facilitate collaboration and knowledge sharing across different teams.
- Strong Culture. A strong culture can support any system. But it's essential to align one with the desired culture.
The optimal organizational structure type is one that:
- Aligns with the strategic goals
- Supports its operations
- Empowers its employees
By considering the factors outlined above, companies can select a system that will enable them to thrive in a competitive marketplace.
Remember, the best